Smoking causes fatal diseases as well as creating a carcinogenic soup in your mouth that could lead to oral cancer….find out more here…
Q How can smoking affect my oral health?
A Most people are now aware that smoking is bad for our health. It can cause many different medical problems and, in some cases, fatal diseases. However, many people dont realise the damage that smoking does to their mouth, gums and teeth.
Smoking can lead to tooth staining, gum disease, tooth loss and in more severe cases mouth cancer.
Q Why are my teeth stained?
A One of the effects of smoking is staining on the teeth due to the nicotine and tar content. It can make the teeth yellow in a very short time, and heavy smokers often complain that their teeth are almost brown after years of smoking.
Q How will smoking affect my gums and teeth?
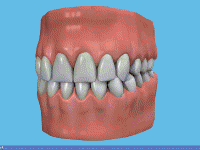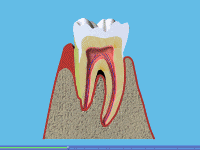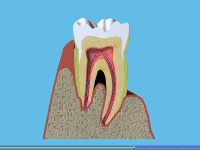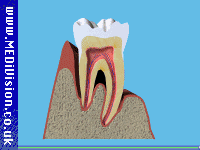
A Smoking can also lead to gum disease. Patients who smoke are more likely to produce bacterial plaque, which leads to gum disease. The gums are affected because smoking causes a lack of oxygen in the bloodstream, so the infected gums fail to heal. Smoking causes people to have more dental plaque and for gum disease to progress more rapidly than in non-smokers. Gum disease still remains the most common cause of tooth loss in adults.
Q How is smoking linked with cancer?
A Most people know that smoking can cause lung and throat cancer, but many people are still unaware that it is one of the main causes of mouth cancer too. Every year thousands of people die from mouth cancer brought on by smoking. (See our leaflet Tell Me About Mouth Cancer)
Q Are there special dental products I can use?
A There are special toothpastes for people who smoke. They are sometimes a little more abrasive than ordinary pastes and should be used with care. Your dentist may recommend that you use these toothpastes alternately with your usual toothpaste. As there are several toothpastes on the market which claim to whiten teeth it is important to look for those accredited by the British Dental Health Foundation. Our logo means that the claims on the packaging are scientifically proven to be correct and the product will be effective at removing staining caused by smoking.
Q What about mouthwashes?
A People who smoke may find they are more likely to have bad breath than non-smokers. Fresh breath products such as mouthwashes may help to disguise the problem in the short term, but will only mask it.
Q How often should I visit my dentist?
A It is important that you visit your dentist regularly both for a normal check up and a full mouth examination so that any other conditions can be spotted early.
You should visit your dentist at least once a year. However, this may be more often if your dentist feels it necessary. People who smoke are more likely to have stained teeth, and therefore may need appointments more often with the dental hygienist.
Q What can my dentist do for me?
A Your dentist will carry out a regular examination to make sure that your teeth and gums and whole mouth are healthy.
Your dentist will also examine your cheeks, tongue and throat for any signs of other conditions that may need more investigation.
They may also be able to put you in touch with organisations and self- help groups who will have the latest information to help you stop smoking.
Q Will I need any extra treatment?
A Your dentist may also refer you to a dental hygienist, for further treatment, thorough cleaning and to keep a closer check on your oral hygiene.
Your dental hygienist will be able to advise you on how often you should visit them, although this should usually be every three to six months.